 bevictor伟德中文副教授。主要研究方向大气污染,气溶胶非均相化学,大气模式中的沙尘和生物质燃烧气溶胶模拟等。在武汉大学获得摄影测量与遥感学士及硕士学位,在美国田纳西大学获得环境工程博士学位。
bevictor伟德中文副教授。主要研究方向大气污染,气溶胶非均相化学,大气模式中的沙尘和生物质燃烧气溶胶模拟等。在武汉大学获得摄影测量与遥感学士及硕士学位,在美国田纳西大学获得环境工程博士学位。
Xinyi Dong is an Associate Professor in the Department of Atmospheric Science at Nanjing University. The focus of Xinyi's reearch work include atmospheric modeling of interactions between natural dust, biogenic VOCs and anthropogenic pollutants. Currently, my research team is utilizing multiple models including CAM-chem, GEOS-Chem, and WRF-Chem to understand the formation mechanisms of secondary aerosols (organic and inorganic) and their impacts on air pollution and climate.
联系方式 (Contact Information)
dongxy@nju.edu.cn
工作经历 (Employment)
2020 至今 bevictor伟德 副教授 Associate Professor
2016-2020 田纳西大学 博士后 Post-Doctoral Research Assistant
教育背景(Education)
2010-2015 美国田纳西大学环境工程 博士 Ph.D. in Environmental Engineering - Univ. of Tennessee
2006-2008 武汉大学摄影测量与遥感 硕士 M.Sc. in Photogeometry and Remote Sensing - Wuhan Univ.
2002-2006 武汉大学摄影测量与遥感 本科 B.Sc. in Photogeometry and Remote Sensing - Wuhan Univ.
研究方向 (Research Interest)
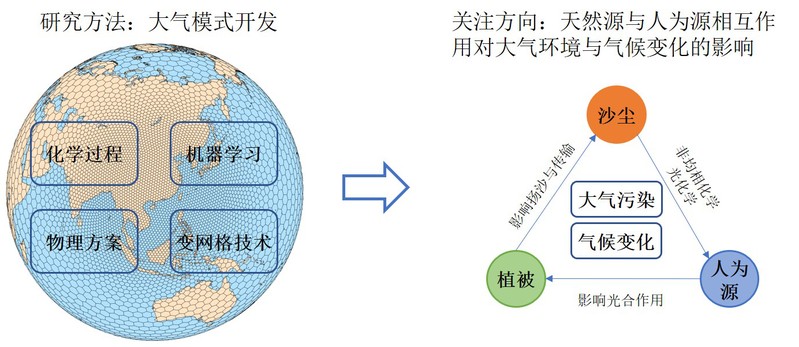
• 天然源(沙尘、植被、野火)与人为源排放相互作用过程
• 大气模式开发:GEOS-Chem,CAM-Chem,CMAQ,WRF-VPRM
• 气溶胶化学:沙尘非均相化学,天然源VOCs气态化学,液相化学
科研项目 (Research Project)
2024-2027 科技部重点专项课题“硫氮碳跨介质交还对大气污染生消及陆地生态系统的影响”,参与
2024-2024 关键地球物质循环前沿科学中心GeoX重点项目“基于地球系统模式的沙尘铁生物地球化学循环研究”,主持
2024-2027 科技部重点研发计划“下一代碳卫星及全球碳盘点遥感科学产品与应用”,参与
2024-2026 国家自然科学基金国际合作项目“亚洲沙尘的大气污染效应及气候变化下的应对性策略研究”,参与
2024-2025 科技部重点研发计划政府间重点专项“污碳协同响应建模及环境-气候风险融合分析”,参与
2023-2023 关键地球物质循环前沿科学中心GeoX培育项目“沙尘铁生物地球化学循与气候系统相互作用”,主持
2021-2024 国家自然科学基金面上项目“沙尘非均相化学大气模式开发与模拟研究”,主持
2021-2021 关键地球物质循环前沿科学中心青年教师项目“沙尘铁生物地球化学循环模式开发”,主持
课程教学 (Courses)
本科-《计算方法》 秋季学期
本科-《气候与全球变化科学基础》 春季学期
本科-《Introduction to Environmental Science》 秋季学期
研究生-《Carbon Emission and Carbon Neutrality》 秋季学期
研究生-《Earth System Modeling》 秋季学期
Recent Publications
2025
59. Zhu, H., Liu, Y., Yue, M., Feng, S., Fu, P., Huang, K., Dong, X., and Wang, M.: Trends and drivers of soluble iron deposition from East Asian dust to the Northwest Pacific: a springtime analysis (2001–2017), Atmos. Chem. Phys., 25, 5175–5197, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-25-5175-2025, 2025.
58. Liu, Y., Li, X., Ge, Q. et al. Carbonate radical ion as a key driver of rapid atmospheric sulfate formation. npj Clim Atmos Sci 8, 45 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-025-00905-4
57. Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Yue, M., Dong, X., Huang, K., and Wang, M.: Understanding the long-term trend of organic aerosol and the influences from anthropogenic emission and regional climate change in China, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 25, 3857–3872, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-25-3857-2025, 2025
56. Lan Luo, Xintong Wu, Jie Hu, Xinyi Dong, Haikun Wang, Assessing the environmental and economic impacts of intracity express delivery: Pathways for carbon reduction and cost efficiency in China, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, Volume 212,107989, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107989.
2024
55. Yue, M., Liu, Y., Wang, M., Dong, X.,Emmons, L. K., & Liang, Y. (2024).Weakened aerosol‐PBL interactionsenhance future air quality benefits undercarbon neutrality in China: Insights fromthe advanced variable‐resolution globalmodel. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 129, e2024JD041106.https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD041106
54. Shao, X., Wang, M., Dong, X., Liu, Y., Shen, W., Arnold, S., Regayre, L., Andreae, M., Pöhlker, M., Jo, D., Yue, M., and Carslaw, K.: Global modeling of aerosol nucleation with an explicit chemical mechanism for highly oxygenated organic molecules (HOMs), Atmos. Chem. Phys., 24, 11365–11389, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-24-11365-2024
53. Li, X., Yu, Z., Yue, M., Liu, Y., Huang, K.,Chi, X., et al. (2024). Modeling study on the impacts of mineral dust photocatalytic heterogeneous chemistry on the sulfur removal over East Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 129,e2024JD041560. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD041560
52. Wenxiang Shen,Minghuai Wang,Xinyi Dong,Enhanced Aging of Black Carbon under Recent Clean Air Actions and Future Carbon Neutrality Scenario in China,Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 31, 13697–13706
51. Lingyao Dong, Minghuai Wang, Daniel Rosenfeld, Yannian Zhu, Yuan Wang, Xinyi Dong, Zhoukun Liu, Hao Wang, Yi Zeng, Yang Cao, Xin Lu, Jihu Liu, Wenxiang Shen:Effects of smoke on marine low clouds and radiation during 2020 western United States wildfires,Atmospheric Research,302,2024,107295,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2024.107295.
50. Flood, V. A., Strong, K., Whaley, C. H., Walker, K. A., Blumenstock, T., Hannigan, J. W., Mellqvist, J., Notholt, J., Palm, M., Röhling, A. N., Arnold, S., Beagley, S., Chien, R.-Y., Christensen, J., Deushi, M., Dobricic, S., Dong, X., Fu, J. S., Gauss, M., Gong, W., Langner, J., Law, K. S., Marelle, L., Onishi, T., Oshima, N., Plummer, D. A., Pozzoli, L., Raut, J.-C., Thomas, M. A., Tsyro, S., and Turnock, S.: Evaluating modelled tropospheric columns of CH4, CO, and O3 in the Arctic using ground-based Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) measurements, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 24, 1079–1118, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-24-1079-2024, 2024.
49. Shen, W., Wang, M., Riemer, N., Zheng, Z., Liu, Y., & Dong, X. (2024). Improving BC mixing state and CCN activity representation with machine learning in the community atmosphere model version6 (CAM6). Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 16, e2023MS003889. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023MS003889
毕业员工:
本科(去向):程曼秋(2016级,北京大学直博在读)、刘琪(2017级,就职新东方)、张凌(2018级,就职TPLink)、李正非(2018级,就职华为)、王梓峻(2019级,就职新城控股)、黄睿(2019级,bevictor伟德研究生在读)、李由(2020级,就职重庆公务员)、熊易(2021级,康奈尔大学读博)
研究生(去向):刘雅曼(2018博,就职中国气科院青山湖分院)、黄如琦(2021硕,就职湖南省气象局)、李晓(2021博,就职南京信息工程大学)、张雯欣(2022硕,bevictor伟德读博)、孔子漩(2023硕、bevictor伟德读博)
